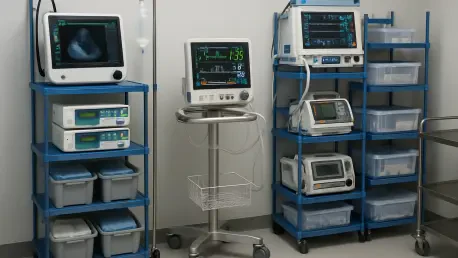
In the intricate and high-stakes environment of modern healthcare, where every second and every resource can profoundly impact patient outcomes, the management of physical assets has transformed from a mundane logistical task into a critical strategic function. This evolution is driven by a convergence of immense global pressures, including rising operational costs, shrinking service capacity, and an unrelenting public demand for higher quality and safer care. Hospitals and healthcare systems are increasingly recognizing that the efficient tracking, maintenance, and optimization of their entire inventory of medical equipment—from infusion pumps and ventilators to wheelchairs and diagnostic machines—is no longer an optional efficiency project but a foundational element of financial stability and clinical excellence. The core question has shifted from whether organizations can afford to implement sophisticated asset management systems to whether they can truly afford the immense clinical and financial risks of neglecting to do so.
The Growing Imperative for Resource Optimization
An examination of the global healthcare landscape reveals a system operating under significant and sustained pressure, a reality substantiated by key performance indicators from international bodies. Data from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) shows a long-term trend of declining hospital bed density, which averaged just 4.2 beds per 1,000 population across member countries in 2023, indicating a shrinking per-capita capacity for inpatient care. This is compounded by acute-care hospital occupancy rates that average 72 percent and frequently surge into risk zones where capacity is dangerously strained. This leaves many health systems with a minimal margin for error when faced with public health crises or seasonal demand spikes. The uneven global distribution of facilities further creates pockets of severe resource scarcity, magnifying the impact of any inefficiency. In this constrained environment, the traditional tolerance for underutilized, misplaced, or poorly maintained equipment has evaporated, making strategic asset management an essential tool for survival and growth.
Within this challenging context, healthcare providers must extract the maximum possible value and operational uptime from every existing asset to enhance system resilience without relying solely on massive capital investments in new infrastructure. Inefficiencies, such as those identified in studies of public hospital networks where many facilities operate below optimal efficiency, represent a significant drain on already limited resources. These studies empirically confirm the urgent need for systems that can systematically identify and correct the underutilization of critical equipment, suboptimal resource allocation between departments, and inadequate maintenance protocols that lead to premature failure. Healthcare Asset Management (HAM) directly confronts these systemic weaknesses by establishing a framework for accountability, real-time traceability, and optimized deployment. The market’s robust projected growth, from USD 19.49 billion in 2024 to an estimated USD 120.89 billion by 2032, reflects a powerful industry consensus on the escalating criticality of these solutions.
The Digital Transformation of Asset Management
The efficacy of contemporary Healthcare Asset Management is rooted in a sophisticated and synergistic blend of hardware and software technologies designed to create a comprehensive, real-time digital twin of a hospital’s entire asset landscape. The foundational layer of this technological ecosystem is composed of Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) and the Internet of Things (IoT). By affixing small, durable tags or sensors—such as Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tags or Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons—to mobile medical devices, hospitals can automate location tracking with remarkable accuracy. This technology virtually eliminates the time-consuming and frustrating manual searches for equipment that plague clinical staff, reduces the common practice of equipment hoarding by individual departments worried about availability, and provides a clear, map-based visual interface showing the precise location of every tagged asset. This constant stream of location data forms the bedrock upon which all higher-level management and analytical functions are built.
This powerful hardware infrastructure feeds a continuous stream of data into a centralized software platform that acts as the system’s command center. This software manages a comprehensive asset database containing crucial information for each item, including its purchase date, warranty details, complete maintenance history, and calibration schedules. The platform automates the creation and assignment of work orders for preventive maintenance, basing schedules not on arbitrary timelines but on manufacturer recommendations or, increasingly, on actual usage data captured by the IoT sensors. This proactive approach ensures equipment reliability and significantly extends its operational lifespan. Furthermore, this layer transforms raw operational data into actionable strategic intelligence. Administrators can access intuitive dashboards that visualize key metrics such as utilization rates by device type, departmental usage patterns, average equipment downtime, and the total cost of ownership, enabling an evidence-based approach to decision-making.
A Cascade of Interconnected Organizational Benefits
The implementation of a robust HAM system yields a wide spectrum of tangible benefits that create a positive ripple effect throughout an organization, impacting everything from the balance sheet to the patient bedside. One of the most significant advantages lies in maximizing resource utilization and capital efficiency. In an environment defined by limited beds and constrained budgets, HAM ensures that expensive medical devices do not sit idle in a supply closet while another department is in critical need. By identifying underutilized equipment through data analysis, hospitals can facilitate seamless sharing between departments or even across different facilities within a larger health network. This strategic reallocation avoids unnecessary duplicate purchases, conserves precious capital for other critical investments, and ensures that the organization derives the maximum possible return from its existing asset base. This data-driven approach to procurement and capital planning is a powerful tool for achieving long-term financial sustainability.
Beyond the clear financial advantages, the impact of effective asset management on daily operations and clinical quality is profound. A primary source of inefficiency and frustration in hospitals is the significant amount of time clinical staff waste searching for necessary equipment. RTLS and other tracking technologies drastically reduce this non-value-added “search time,” liberating nurses, technicians, and physicians to focus on their primary, patient-facing responsibilities. This seemingly simple change boosts staff morale, improves patient throughput by reducing delays in diagnosis and treatment, and enhances overall operational flow. Concurrently, automated and usage-based preventive maintenance scheduling dramatically reduces the risk of unexpected equipment failure during critical medical procedures. This is particularly vital for life-support and diagnostic machinery in intensive care units and emergency departments, where reliable equipment can be the difference between life and death. This directly translates to more consistent and safer patient care, while the centralized digital log of all maintenance activities provides an unimpeachable, auditable trail for regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
Navigating the Hurdles to Implementation
Despite the compelling value proposition, several significant barriers can hinder the widespread adoption of comprehensive HAM systems, requiring careful strategic planning to overcome. The most prominent challenge is often the substantial upfront financial investment. The combined cost of hardware like tags and sensors, software licenses, system integration with existing IT infrastructure, and comprehensive staff training can be a formidable obstacle, particularly for smaller, independent hospitals or those operating in low-resource settings. Decision-makers must conduct a thorough return on investment analysis that accounts not only for direct cost savings from reduced capital expenditure but also for the softer, yet equally important, gains in staff productivity and patient safety. Without a clear financial roadmap and strong executive sponsorship, securing the necessary budget for such a transformative project can be difficult.
Beyond the initial investment, healthcare organizations frequently encounter complex technical and cultural challenges during implementation. Many hospitals operate with outdated, fragmented IT systems and deeply ingrained, siloed departmental workflows. Integrating a modern, centralized HAM platform with these legacy systems can be a technically complex and resource-intensive endeavor, requiring specialized expertise. However, perhaps the most critical success factor is effective change management and staff adoption. The ultimate value of a HAM system depends on its consistent and correct use by frontline clinical and operational staff. This necessitates not just initial training but also a concerted effort to foster a cultural shift toward data-driven asset stewardship. Overcoming resistance to new workflows and addressing any perception of an added administrative burden are crucial steps to ensure that the system is embraced as a valuable tool rather than viewed as an unwelcome mandate.
Forging a Path Toward Strategic Asset Stewardship
This analysis positioned Healthcare Asset Management not as an optional technological upgrade but as a foundational component of modern, resilient, and efficient healthcare delivery. To accelerate its adoption and unlock its full potential, a multi-pronged approach involving a partnership between policymakers, providers, and technology vendors was deemed necessary. It was noted that policymakers and accrediting bodies had a crucial role to play by integrating robust asset management standards into hospital accreditation requirements. They could also provide targeted financial incentives, such as grants or subsidies, to help healthcare organizations offset the initial implementation costs, particularly for those serving vulnerable populations. In parallel, large healthcare systems with multiple facilities were identified as being uniquely positioned to achieve significant economies of scale by deploying centralized HAM platforms, which enabled cross-facility resource sharing and the optimization of asset distribution across an entire network.
Looking toward the future, the evolution of HAM was expected to continue its rapid trajectory, driven by persistent advances in the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. The discussion moved beyond simple location tracking to envision a future centered on predictive maintenance, where sophisticated algorithms would analyze real-time usage and performance data to forecast potential equipment failures before they occurred, allowing for proactive intervention. Deeper integration with clinical and supply-chain systems promised to create a fully connected healthcare ecosystem, providing unprecedented insights into the relationship between asset availability, patient care pathways, and overall operational costs. Ultimately, the deliberate embrace of strategic asset management was presented as the most effective path for hospitals and health systems to navigate the challenges of a resource-constrained world, ensuring they operated more efficiently, delivered safer care, and made the wisest possible use of every resource to improve patient outcomes.