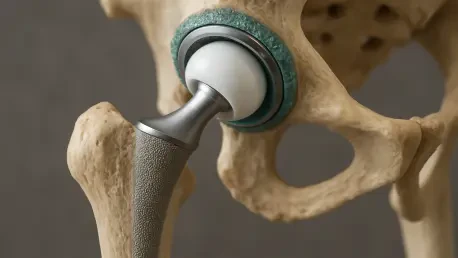
In the realm of orthopedic advancements, a staggering challenge looms over hip replacement surgeries: the risk of post-surgical infections that, though rare, can turn deadly with alarming consequences for patients, affecting just 1% to 2% of primary hip replacement cases. These infections carry a three-year mortality rate of 11%, casting a shadow over an otherwise transformative procedure. Zimmer Biomet, a titan in the orthopedic device industry, has recently achieved a significant milestone by securing breakthrough device designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its innovative iodine-treated total hip replacement system. Designed to combat bacterial growth and biofilm formation, this technology promises a new frontier in patient safety. By integrating a controlled-release iodine layer into its Taperloc Complete Hip System, the company aims to address a critical healthcare issue, offering hope to high-risk patients and potentially reshaping infection prevention strategies in joint replacement surgeries across the globe.
Pioneering Infection Prevention in Orthopedics
Hip replacement surgeries, while often life-changing, come with the hidden peril of infections that can devastate patient outcomes, making preventative innovations a pressing need in modern medicine. Zimmer Biomet’s latest breakthrough centers on a novel approach using iodine, a well-known antimicrobial agent, integrated into the surface of its hip implants through advanced anodization and electrophoresis techniques. This controlled-release layer is engineered to inhibit bacterial growth and prevent the formation of biofilms—stubborn bacterial colonies that resist conventional treatments and often necessitate implant removal. What sets iodine apart is not only its effectiveness against a wide range of bacteria but also its inability to contribute to antibiotic resistance, a growing global concern. Additionally, iodine’s established safety profile in medical applications adds to its appeal as a game-changer. This technology targets the root cause of post-surgical complications, potentially reducing the severe consequences faced by a small but vulnerable percentage of patients undergoing hip replacements.
Beyond the technical innovation, the significance of this development lies in its potential to redefine patient care standards within the orthopedic field, addressing a critical gap in current practices. Infections following joint replacements often lead to prolonged hospital stays, additional surgeries, and, in the worst cases, tragic outcomes, placing immense physical and emotional burdens on patients. Zimmer Biomet’s iodine-treated implant represents a shift toward proactive solutions rather than reactive treatments, aligning with a broader industry push to prioritize prevention over cure. By focusing on high-risk patients who are more susceptible to infections due to underlying conditions or prior medical history, this technology could offer a tailored safeguard, enhancing recovery prospects. The integration of such advanced surface treatments into standard implants also signals a departure from traditional reliance on systemic antibiotics, which can be less effective against localized implant infections. This approach underscores a growing recognition that innovative materials and coatings may hold the key to safer surgical outcomes in the evolving landscape of medical devices.
Regulatory Milestones and Market Strategies
Securing the FDA’s breakthrough device designation marks a pivotal moment for Zimmer Biomet, as it opens doors to expedited regulatory support and a faster path to bringing its anti-infection hip technology to American patients facing significant health risks. This designation, part of a specialized FDA program, facilitates closer collaboration during the premarket review phase, allowing for streamlined feedback and potentially shaving critical time off the approval process. Such regulatory backing is vital for navigating the complex landscape of medical device approvals in the U.S., where rigorous standards must be met to ensure patient safety. Already, the iodine-treated implant has gained traction internationally, with approval in Japan signaling early validation of its efficacy and market potential. This dual progress highlights Zimmer Biomet’s strategic focus on global expansion while prioritizing the U.S. market, where demand for safer orthopedic solutions continues to grow amid rising surgical volumes and an aging population.
However, the journey to market is not without its hurdles, as past experiences with anti-infection technologies have shown the intricate balance between innovation and regulatory challenges for Zimmer Biomet. A prior collaboration aimed at developing infection-preventing implants encountered significant delays in achieving U.S. approval, despite some achievements in European markets, ultimately leading to the dissolution of an expanded agreement a few years ago. This history serves as a reminder of the unpredictable nature of introducing novel medical technologies in a highly scrutinized environment. The current FDA breakthrough status, therefore, is not just a step forward but also a chance to overcome previous setbacks, though uncertainties linger about the final timeline for market entry. The company’s leadership has expressed confidence in a viable pathway to approval, even as specific regulatory perspectives remain undisclosed in public discussions. This cautious optimism reflects a broader understanding that while the technology holds immense promise, its ultimate success hinges on meticulous execution and regulatory alignment.
Industry Trends and Future Implications
The development of Zimmer Biomet’s iodine-coated hip implant is emblematic of a wider movement within the orthopedic industry to tackle post-operative infections through cutting-edge preventative technologies rather than relying solely on post-infection interventions. Research and innovation in surface treatments, such as antimicrobial coatings, have gained momentum as stakeholders recognize the high stakes of infection-related complications, which can derail patient recovery and inflate healthcare costs. This trend is fueled by the limitations of existing solutions, where systemic treatments often fall short against localized bacterial challenges on implant surfaces. Drawing on foundational studies from regions like Japan, the global collaborative effort to address this issue is evident, with companies increasingly investing in materials science to enhance implant safety. Zimmer Biomet’s work positions it at the forefront of this shift, potentially setting a new benchmark for how joint replacement devices are designed to prioritize infection resistance from the outset.
Looking ahead, the implications of this technology extend beyond a single product, hinting at a transformative era for orthopedic care where infection prevention becomes an integral part of implant design across various surgical applications. If successful, Zimmer Biomet’s iodine-treated system could inspire similar innovations for other joint replacements, such as knees or shoulders, where infection risks also pose significant threats. The FDA’s support through the breakthrough designation not only aids this specific project but also sends a signal to the industry about the value of investing in preventative solutions. However, the road to widespread adoption will likely involve addressing cost considerations, scalability of production, and long-term clinical data to confirm efficacy. As the medical device sector continues to evolve, the focus on integrating antimicrobial technologies could redefine patient outcomes, reducing the shadow of infection over life-enhancing surgeries and fostering greater trust in orthopedic interventions among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Reflecting on a Path Forward
Looking back, Zimmer Biomet’s pursuit of an iodine-treated hip replacement system stood as a bold response to the persistent threat of post-surgical infections, a rare yet devastating complication in orthopedic care. The achievement of FDA breakthrough status marked a crucial chapter, having provided enhanced regulatory collaboration that aimed to hasten the technology’s availability to U.S. patients. Building on earlier approval in Japan, the innovation showcased the power of global insights and iodine’s antimicrobial strengths. Yet, past struggles with similar anti-infection efforts reminded all of the intricate dance between groundbreaking ideas and regulatory realities. Moving forward, the focus shifted to rigorous clinical validation and strategic market planning to ensure this technology reached those in need. Stakeholders across the industry were encouraged to monitor long-term outcomes and advocate for broader adoption of preventative designs, paving the way for safer surgical futures while addressing remaining challenges with precision and resolve.