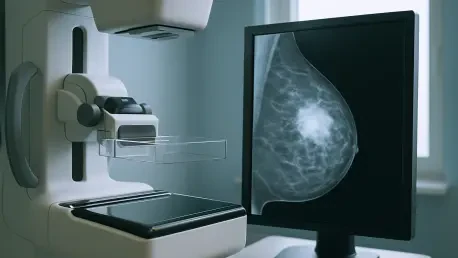
In an era where technology continually reshapes the medical landscape, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in enhancing breast cancer screening represents a significant leap forward in diagnostic precision. AI systems, often described as an “additional set of eyes,” are becoming indispensable in interpreting mammograms with heightened accuracy and efficiency. These advancements are crucial, given that early detection significantly influences the prognosis and treatment of breast cancer. For radiologists, integrating AI into their practice translates into improved reading patterns and higher cancer detection rates without prolonging the diagnostic process. Such shifts underscore the symbiotic relationship between human expertise and AI capabilities in medical imaging—a partnership that enhances the overall quality of healthcare delivery. However, utilizing AI in this capacity raises questions about dependency and critical oversight, as both human judgment and machine intelligence must operate in concert to avoid potential misdiagnoses and unwarranted recalls.
Integrating AI into Breast Cancer Screening
AI’s integration into mammogram analysis marks a transformative phase in radiological practices, significantly improving the accuracy and efficiency of breast cancer detection. Radiologists utilizing AI decision support systems report notably enhanced cancer detection rates compared to traditional methods. AI’s capacity to pinpoint areas of interest on mammograms allows radiologists to refine their focus, thereby optimizing reading patterns and reducing the likelihood of oversight during image interpretation. The study highlights how AI effectively guides radiologists through the evaluation process by acting as an adjunct to human analysis. For instance, in scenarios where AI identifies low-risk areas, it aids radiologists in confidently reinforcing decisions not to recall patients unnecessarily. This judicious application of AI contributes to the early detection of cancerous lesions, ultimately transforming patient outcomes.
Furthermore, AI not only assists in highlighting potential anomalies but also influences visual search patterns, prompting radiologists to scrutinize suspicious areas with increased diligence. By drawing attention to specific regions, AI helps avoid the pitfalls of oversight which may result from sheer volume and fatigue. Eye-tracking studies illustrate this dynamic, showing how AI-generated suggestions lead to more focused observation on critical imaging zones. The technology functions almost like an auxiliary perspective, enhancing decision-making processes through refined image scrutiny. Radiologists equipped with AI tools can thus deliver diagnoses with improved confidence, knowing that their assessments are backed by machine-generated insights that complement their expertise. This blend of AI and human capacity ensures a thorough examination, promoting a balance between technological innovation and clinical judgment.
Balancing AI Utility with Clinical Expertise
Despite the advantages AI introduces in breast cancer screening, caution is advised to prevent an overreliance on AI-generated information which might result in harmful outcomes. It is essential for radiologists to apply critical thinking to AI outputs to counteract misleading machine-generated suggestions. This skepticism acts as a safeguard against potential errors, ensuring that AI serves as a supplemental tool rather than a primary decision-maker. Acknowledging the limitations of AI is vital, as these systems can occasionally present false positives or negatives that, if taken at face value, might lead to unwarranted patient anxiety or overlooked diagnoses. Therein lies the balance: maintaining confidence in AI while ensuring radiologists remain vigilant and decisive in their practice.
Instituting robust educational programs is key in equipping radiologists with the acumen to discern effectively when and how to leverage AI amidst patient evaluations. Training initiatives focusing on both AI functionality and the nuances of radiological practice ensure that healthcare professionals are prepared to integrate AI seamlessly into their diagnostic workflow. By honing these skills, radiologists can elevate their interpretative accuracy and foster an environment where AI is viewed as a collaborative partner rather than an infallible authority. Additionally, research into the optimal timing for introducing AI insights is being pursued, aiming to boost clinical efficiency by identifying when AI can be most beneficial, without overwhelming the diagnostic process with premature or excessive data.
Navigating AI’s Role in Future Diagnostics
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of breast cancer screening by significantly improving diagnostic accuracy. AI, often seen as an “additional set of eyes,” is now essential for interpreting mammograms, delivering results with enhanced precision and speed. This technological advance is crucial because early detection of breast cancer plays a pivotal role in determining treatment outcomes and patient prognosis. For radiologists, integrating AI into their workflows means they can identify cancer more accurately without extending the time needed for diagnosis. This development highlights the beneficial partnership between human expertise and AI capabilities in medical imaging, ultimately elevating the quality of healthcare delivery. However, the reliance on AI in this domain does prompt concerns about dependency and the need for critical oversight. It’s essential for human judgment and machine learning to work together to prevent potential misdiagnoses and unnecessary follow-ups, ensuring optimal patient care.