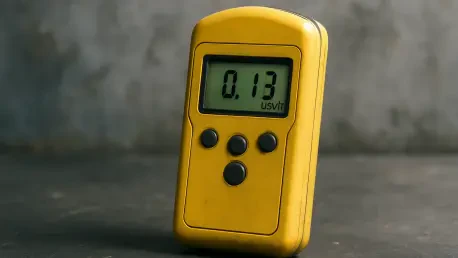The silent and invisible nature of ionizing radiation presents a persistent challenge across numerous high-stakes industries, necessitating sophisticated technology to ensure safety and operational integrity. Responding to this critical need, the global radiation detection market is on a trajectory of significant expansion, with projections indicating its value will climb to an estimated US$2,649.2 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5%. This robust growth is fundamentally driven by the expanding use of radioactive materials and advanced radiation-emitting equipment in sectors ranging from healthcare to national defense. As reliance on these powerful tools increases, so does the imperative for precise, reliable, and compliant detection systems. These devices are no longer niche instruments but have become essential components of the safety infrastructure that underpins modern technological progress, safeguarding both personnel and the public while ensuring the accuracy of critical processes. The market’s upward trend is a direct reflection of a global commitment to harnessing the benefits of nuclear technology responsibly.
Healthcare Applications as a Primary Growth Catalyst
The medical field stands out as a powerful engine for the radiation detector market, propelled by the relentless advancement and adoption of diagnostic and therapeutic technologies. Modern healthcare increasingly relies on applications that utilize ionizing radiation, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and sophisticated radiotherapy techniques for cancer treatment. In these environments, radiation detectors are indispensable, serving a dual purpose: they protect patients and medical professionals from unnecessary exposure and ensure the precise delivery of radiation doses, which is paramount for effective treatment and accurate diagnosis. Nuclear medicine, which involves administering radiopharmaceuticals for both imaging and therapy, further amplifies this demand. The expansion of healthcare infrastructure worldwide, coupled with a rising incidence of diseases like cancer that necessitate radiation-based interventions, creates a consistent and growing need for these monitoring systems. Consequently, hospitals and clinics are continuously investing in state-of-the-art detection equipment to meet stringent regulatory standards and uphold the highest levels of patient care and occupational safety.
Heightened Safety Imperatives and Industrial Demand
A heightened global consciousness regarding the long-term risks of radiation exposure serves as another significant driver for the market. Landmark nuclear incidents, such as those at Chernobyl and Fukushima, have left an indelible mark on public and regulatory perception, underscoring the severe health consequences, including an increased prevalence of various cancers, that can result from uncontrolled radiation release. These events have catalyzed substantial investment in comprehensive monitoring and safety protocols, not only within the nuclear power industry but also in adjacent sectors. The defense industry, for instance, requires robust detection systems for monitoring nuclear stockpiles and ensuring the safety of personnel. Likewise, various industrial applications, including materials testing and sterilization processes, utilize radioactive sources and demand rigorous safety oversight. This pervasive focus on safety and regulatory compliance ensures a steady demand for a wide array of radiation detection technologies capable of providing early warnings and accurate measurements in diverse operational settings, from power plants to research laboratories.
The technological landscape of the radiation detection market is currently dominated by established and reliable solutions, with gas-filled detectors being a notable leader. This category, which includes well-known devices like Geiger-Muller counters, has maintained its prominence due to a compelling combination of cost-effectiveness and broad applicability. Their ability to reliably detect alpha, beta, and gamma radiation makes them versatile tools suitable for a multitude of tasks, from routine contamination checks in a laboratory to large-scale environmental monitoring. While more advanced and specialized detectors, such as scintillators and semiconductor-based devices, offer higher sensitivity or energy resolution for specific applications, the straightforward operation and economic feasibility of gas-filled detectors ensure their continued widespread adoption across the healthcare, industrial, and defense sectors. Their enduring market leadership illustrates a preference for proven, practical technology that can be deployed at scale to meet the fundamental requirements of radiation safety and monitoring across an expanding range of fields.
A Legacy of Enhanced Global Safety
The sustained growth in the radiation detector market ultimately forged a new global standard for safety and operational excellence across all sectors utilizing ionizing radiation. The period leading up to 2030 was characterized by a proactive integration of advanced monitoring systems, driven by lessons from the past and the demands of technological innovation. This widespread adoption did more than just fulfill regulatory mandates; it cultivated a deep-rooted culture of safety that prioritized the well-being of workers and the public. Industries that once viewed radiation monitoring as a compliance necessity came to recognize it as a cornerstone of responsible and sustainable operation. The advancements in detector technology, from more sensitive scintillators to more robust and affordable gas-filled counters, provided a versatile toolkit that empowered organizations to tailor their safety protocols with unprecedented precision. This era of expansion cemented the role of radiation detection not merely as a market segment, but as an essential pillar of modern technological society.