Picture a future where a doctor can diagnose a life-threatening condition like lung cancer with pinpoint accuracy, using tools so advanced that the procedure feels almost non-invasive. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the reality being shaped by artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics in medical diagnostics today. Once dependent on static imaging methods and labor-intensive manual processes, the field of diagnostics is experiencing a profound shift. These technologies are not only sharpening the precision of disease detection but also redefining patient care by slashing risks and accelerating outcomes. From cutting-edge imaging to tiny robotic devices navigating the human body, the integration of AI and robotics is dismantling barriers that have long hindered early and accurate diagnoses. Yet, as this revolution unfolds, challenges like patient skepticism and ethical dilemmas loom large. Exploring this dynamic landscape reveals how these innovations are paving the way for a new era in healthcare and what obstacles must still be overcome.
Revolutionizing Imaging with Precision Technology
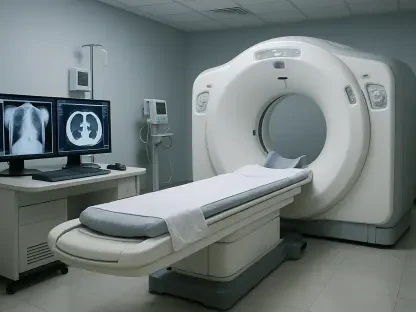
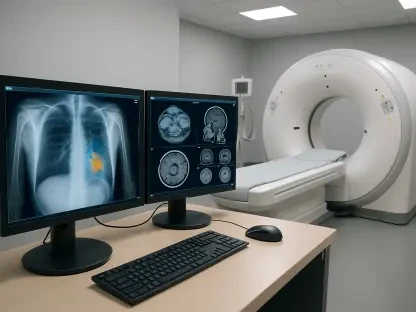
The realm of medical imaging is undergoing a dramatic transformation thanks to the seamless integration of AI and robotics with traditional tools. Methods such as MRI, CT scans, and X-rays, which have remained largely unchanged for decades, are now benefiting from robotic systems that offer unprecedented control. These systems produce high-resolution 3D images while significantly cutting down on patient exposure to harmful radiation. For instance, robotic assistance during scans ensures steadier positioning and finer adjustments, leading to clearer results that can catch abnormalities at earlier stages. This leap forward isn’t just about better pictures—it’s about giving clinicians the ability to detect conditions like tumors or cardiovascular issues before they become critical. The impact on patient outcomes is profound, as early intervention often means less invasive treatments and higher survival rates. As these tools become more refined, the potential to save lives through sharper, safer diagnostics continues to grow.
Beyond the enhancement of image quality, the fusion of AI with imaging technology is streamlining the entire diagnostic process. AI algorithms can analyze scans in real time, identifying subtle patterns or anomalies that might escape even a trained human eye. This capability is particularly valuable in high-pressure environments like emergency rooms, where speed is critical. By reducing the time needed to interpret complex images, AI helps clinicians make faster decisions without sacrificing accuracy. Moreover, robotic systems paired with these algorithms can adapt to individual patient anatomies during procedures, ensuring optimal imaging angles and minimizing errors. While the technology isn’t flawless—requiring robust data to train AI models—it represents a significant step toward automating routine diagnostic tasks. This shift allows medical professionals to focus on patient interaction and complex case management, ultimately enhancing the quality of care delivered across diverse healthcare settings.
Breaking Barriers with Miniaturized Robotic Tools
One of the most remarkable advancements in diagnostics is the development of miniaturized robotic tools capable of navigating the human body’s most challenging terrains. Devices like Intuitive Surgical’s Ion Endoluminal System exemplify this progress, using ultra-thin, flexible instruments to access remote areas such as the lungs for early cancer detection. Unlike traditional methods that often require invasive surgeries, these tools offer a less traumatic alternative, reducing recovery times and patient discomfort. Hospitals employing such systems report improved diagnostic precision, particularly in identifying small, hard-to-reach lesions that might otherwise go unnoticed until advanced stages. The ability to intervene early transforms the prognosis for many life-threatening conditions, offering hope where once there was uncertainty. As these robotic innovations continue to evolve, their role in non-invasive diagnostics is set to expand dramatically.
Another leap forward comes from innovations like pill-sized robotic cameras, which are revolutionizing gastrointestinal imaging. These tiny devices, such as those engineered by Endiatx, can be swallowed and remotely controlled to capture detailed visuals of the digestive tract. Unlike older capsule endoscopy methods that lacked steering capabilities, these modern tools allow clinicians to target specific areas for closer examination. This precision reduces the need for more invasive procedures like traditional endoscopies, which often require sedation and carry higher risks. Patients benefit from a simpler, safer experience while still receiving accurate diagnoses of conditions like ulcers or early-stage cancers. The potential of such technology extends beyond individual care, promising to make diagnostic screening more accessible, especially in underserved regions where advanced medical facilities may be scarce. This democratization of cutting-edge diagnostics marks a pivotal shift in global healthcare equity.
AI as the Catalyst for Diagnostic Innovation
Artificial intelligence stands as a cornerstone in the rapid advancement of medical diagnostics, driving both innovation and accuracy. Platforms like Nvidia’s Isaac for Healthcare create virtual environments to simulate and test robotic surgery and imaging systems, drastically cutting down development timelines. These simulations allow engineers to refine tools under countless scenarios before they ever touch a patient, ensuring safety and effectiveness. Collaborations with industry leaders like GE HealthCare further amplify this impact, integrating AI into real-world applications that enhance diagnostic workflows. From automating routine image analysis to predicting potential complications, AI is freeing up valuable time for clinicians to focus on patient-centered care. The ripple effect of such technology is felt across hospitals, where efficiency gains translate into better resource allocation and shorter wait times for critical diagnoses.
However, the journey of AI in diagnostics is not without its challenges, particularly around data quality and reliability. High-quality training data is essential for AI models to perform accurately, yet obtaining such datasets in healthcare is often difficult due to privacy concerns and limited access to diverse patient information. As a workaround, synthetic or simulated data is increasingly used, though it sparks debate over its suitability for invasive or high-stakes applications. If the data fails to mirror real-world complexities, the risk of diagnostic errors rises, potentially undermining trust in these systems. Addressing this issue requires a delicate balance—leveraging synthetic data to fill gaps while investing in secure, ethical ways to gather real patient information. Until these hurdles are cleared, the full potential of AI-driven diagnostics will remain just out of reach, though the progress made so far signals a promising trajectory for overcoming them.
Navigating Patient Skepticism and Trust Issues
Despite the undeniable benefits of AI and robotics in diagnostics, gaining patient trust remains a formidable barrier to widespread adoption. Many individuals harbor reservations about the safety and reliability of automated or semi-autonomous systems, even when human oversight is involved. Research highlights a disparity in AI performance—while it may surpass general physicians in areas like dermatology, it often falls short of specialists in fields such as gastroenterology. This inconsistency fuels doubts about whether technology can truly replace or complement human expertise in every scenario. For patients, the fear of misdiagnosis or mechanical failure often overshadows the promise of faster, less invasive procedures. Bridging this trust gap is essential for the integration of these tools into routine medical practice, requiring clear communication about their capabilities and limitations.
Compounding the issue of trust is the lingering perception of technology as impersonal or error-prone in critical healthcare settings. Patients accustomed to direct interaction with doctors may feel uneasy relying on machines for something as personal as a diagnosis. Educational efforts to demystify AI and robotic systems can play a vital role in shifting this mindset, emphasizing that these tools are designed to assist, not replace, medical professionals. Highlighting real-world success stories—where robotic diagnostics have caught life-threatening conditions early—can also help ease concerns. Additionally, ensuring transparency about how these systems are developed and tested fosters confidence in their reliability. While fully autonomous diagnostics may not gain acceptance soon, gradual exposure to semi-autonomous tools could pave the way for broader acceptance, reshaping how patients view technology’s role in their care over time.
Ethical Challenges in Data and Development
Ethical considerations add a complex layer to the integration of AI and robotics in diagnostics, particularly concerning data usage. The reliance on synthetic datasets to train AI for invasive tools raises significant questions about their adequacy in replicating real human conditions. If these datasets fail to account for the vast variability in patient anatomies or disease presentations, the resulting diagnostic tools may produce unreliable outcomes. Such risks are especially concerning in high-stakes scenarios where a misstep could have severe consequences. Developers face the challenge of balancing the need for innovation with the responsibility to ensure patient safety, pushing for rigorous validation processes to confirm that AI models perform consistently across diverse populations. This ethical tightrope underscores the importance of prioritizing real-world applicability over expediency in technological advancement.
Another pressing ethical concern lies in maintaining patient privacy while gathering the data necessary to refine these technologies. Medical information is highly sensitive, and any breach could erode public trust in AI-driven diagnostics. Striking a balance between data access for development and safeguarding individual rights demands robust security measures and strict adherence to regulations. Furthermore, transparency about how data is used—whether real or synthetic—can help alleviate fears of misuse or exploitation. As the field progresses, collaboration between technologists, ethicists, and regulators becomes critical to establish guidelines that protect patients while fostering innovation. Addressing these ethical dilemmas head-on is not just a matter of compliance but a foundational step in ensuring that the benefits of AI and robotics are realized without compromising the trust or well-being of those they aim to serve.
Commercial Potential and Intellectual Property Strategies
From a business perspective, the declining cost of robotic systems offers a compelling opportunity for medtech innovators to scale their impact. Over the past decade, prices for industrial robots have halved, making it more feasible for companies to invest in developing and deploying advanced diagnostic tools. This affordability encourages competition and innovation, driving down costs further for healthcare providers and, ultimately, patients. However, with opportunity comes the need for protection—securing intellectual property (IP) rights is paramount to safeguarding these advancements. Patents for both standalone components and integrated systems provide a competitive edge, ensuring that creators can capitalize on their inventions. This strategic focus on IP not only fuels profitability but also incentivizes continued investment in cutting-edge solutions for diagnostics.
The importance of IP protection extends beyond individual technologies to the broader ecosystem of integrated AI and robotic systems. Misconceptions about the patentability of software in certain regions often deter developers, yet robust IP strategies can dispel these myths and secure long-term market positions. A comprehensive patent portfolio acts as a shield against imitation while opening doors to licensing opportunities and partnerships. For companies navigating global markets, this protection is a gateway to sustained growth, allowing them to expand access to life-saving diagnostic tools without fear of losing their edge. As the medtech landscape becomes increasingly competitive, prioritizing IP alongside innovation ensures that the benefits of reduced costs and advanced technology translate into tangible improvements in healthcare delivery, reaching patients across diverse economic and geographic contexts.
Paving the Future: Enhancing Access and Confidence
Looking to the horizon, the trajectory of AI and robotics in diagnostics hinges on building greater familiarity and affordability. As these technologies become more embedded in routine healthcare practices, public hesitation is expected to wane, driven by exposure to their proven benefits. Continued cost reductions will further democratize access, making advanced diagnostics available to a wider range of medical facilities, including those in resource-limited areas. Innovators must focus on user-friendly designs and scalable solutions to ensure that even smaller clinics can adopt these tools without prohibitive financial burdens. This push for accessibility could redefine global health standards, narrowing disparities in diagnostic capabilities and ensuring that early detection becomes a universal possibility rather than a privilege.
Equally vital to this future is the commitment to transparency and reliability in technology development. Addressing societal caution requires consistent demonstration of safety and effectiveness through clinical trials and real-world applications. Developers should engage with healthcare providers to tailor solutions that meet practical needs while maintaining rigorous standards. Partnerships with regulatory bodies can also help establish trust, ensuring that innovations align with patient safety priorities. By focusing on these actionable steps—enhancing access, proving reliability, and fostering confidence—the medtech industry can overcome current barriers. The path forward promises a healthcare landscape where AI and robotics not only transform diagnostics but also empower patients and clinicians alike with tools that are as trusted as they are groundbreaking.